NAAC (National Assessment and Accreditation Council) is an autonomous organization in India established in 1994 by the University Grants Commission (UGC) to assess and accredit higher education institutions.
The primary purpose of NAAC is to evaluate and ensure the quality and standards of higher education in India. NAAC conducts the accreditation of various types of higher education institutions, including universities, colleges, and autonomous institutions. NAAC accreditation is a quality assurance process designed to evaluate and ensure the quality and standards of higher education institutions in India.
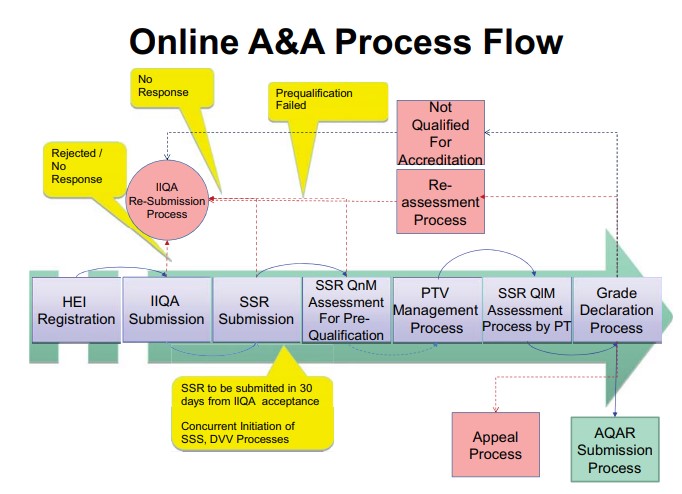
Institutions seeking NAAC accreditation undergo a rigorous assessment process, which includes:
1. the submission of a self-study report
2. an on-site peer review by a team of experts and
3. the evaluation of various criteria related to infrastructure, teaching and learning, research, governance, values and best practices.
The key objectives of NAAC accreditation are:
1. Promoting quality and excellence in higher education.
2. Encouraging institutions to self-evaluate and improve their performance.
3. Providing a framework for continuous improvement in the quality of education.
4. Helping stakeholders make informed decisions about choosing institutions for education.
Significance of NAAC Accreditation
Education is a vital force in a nation’s development, influencing both its progress and the lives of its people. For higher education, both quality and accessibility are crucial. The National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC) was created to ensure these aspects and help institutions enhance their educational standards through a structured process.
1. Self-Improvement: NAAC accreditation guides institutions in identifying their strengths and areas needing improvement. This process encourages them to elevate the quality of their programs, faculty, and infrastructure.
2. Efficient Resource Use: Accreditation helps institutions allocate resources more effectively by highlighting where they are needed most.
3. Collaboration: NAAC promotes teamwork and cooperation among staff, students, and faculty, creating a more dynamic and engaging learning environment.
4. Funding Opportunities: Accredited institutions are more likely to secure funding because they can provide solid evidence of their quality and commitment to improvement.
5. Innovation in Teaching: Accreditation encourages institutions to explore innovative teaching methods, making education more engaging and adaptable to changing needs.
6. Clearer Identity: NAAC accreditation helps institutions set clear goals and objectives, shaping their identity.
7. Trust and Accountability: Accreditation assures students, parents, and society of the quality and accountability of educational institutions.
8. Meeting Employer Expectations: Accredited institutions prepare students with the skills and knowledge employers seek.
9. Collaboration Among Institutions: NAAC accreditation promotes collaboration among educational institutions, allowing them to share best practices and ideas.
NAAC accreditation is vital for improving higher education quality and access. It guides institutions in striving for excellence, benefiting the nation and its people. It’s a commitment to delivering outstanding education.
Criterions & weightage
NAAC has identified a set of seven criteria to serve as the basis of its assessment procedures.
The criterion-wise differential weightages for the three types of HEIs are:
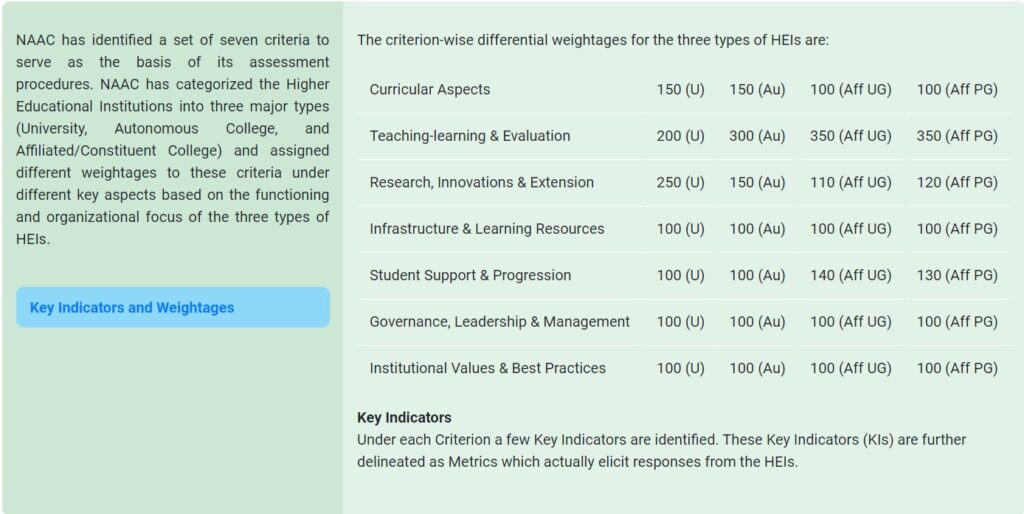
Source: NAAC (http://naac.gov.in/index.php/en/assessment-accreditation)
The final result of the Assessment and Accreditation exercise will be an ICT-based score, which is a combination of evaluation of qualitative and quantitative metrics. This will be compiled as a document comprising three parts.



